Category: Data Science
-
The Intuition Behind Double ML
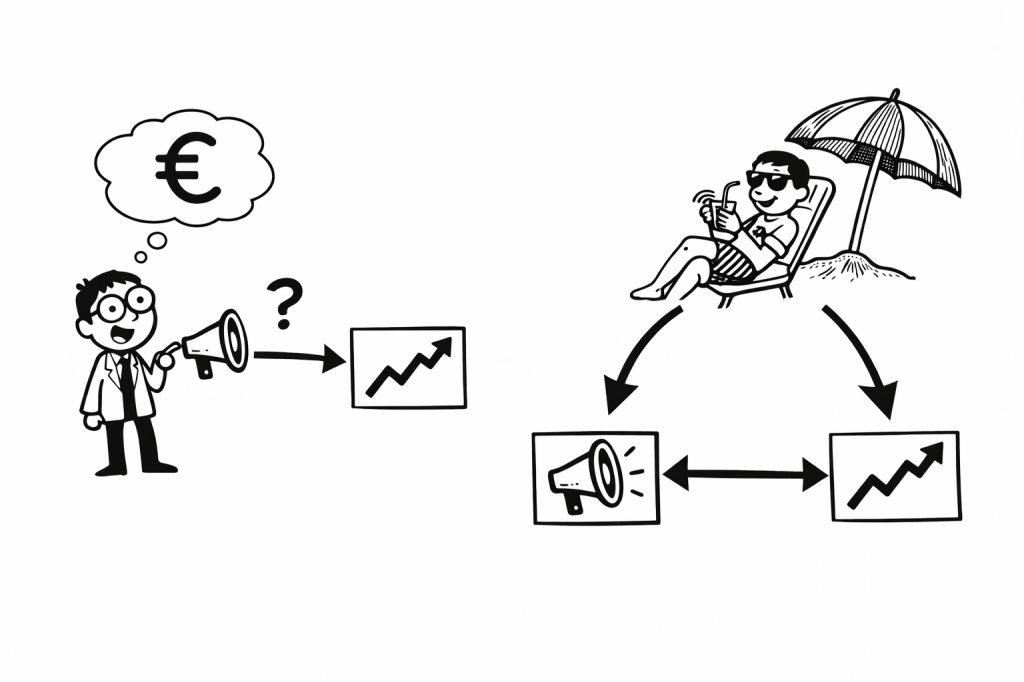
Double Machine Learning (DML or DoubleML) is one of the most powerful, modern techniques in data science & machine learning. However, I often find treatments of the subject a little convoluted, with writers reaching for math or using very particular domain vocabulary. In this article I’m going to drop the math, avoid all the jargon…
-
The Rise of AI Foundation Models

One surprising development, at least to me, in AI is the growing proliferation of foundational models. Text? Sure, makes sense. There’s lots of data out there. Then images, audio, video somehow seemed a natural continuation. But now time series, tabular data, geospatial data, graphs? Foundation models built on public and synthetic data are producing workable…
-
Sketulate: Sketchable Functions & Densities for Data Science

I simulate a lot of data to test my ideas, particularly the more complex ones. With non-standard stuff, it can be pretty time consuming to find the right function and/or parameters to do what I want. If the shape you want isn’t a common function or distribution, you can spend too much time searching for…
-
Calibration Plots with Generalized Additive Models (GAMs)

Calibration of probabilistic predictions is a crucial task in many machine learning applications, especially when the outputs are used downstream for decision-making. It’s actually a simple concept, with calibration just ensuring that the predicted probabilities align with the actual outcomes. Despite that, I’ve noticed many people neglect the step in their modelling process! Typically, when…
-
XGBoost Can’t Extrapolate

A common pattern I observe among inexperienced Data Scientists is the following: they often default to XGBoost or a similar Gradient Boosted Model for their problem without considering whether it’s the right choice for the job. Given how powerful these methods are, this isn’t the most egregious mistake one can make. However, it’s important to…
-
Learn How to Containerize Your R Notebooks with Docker

In this article I show how to containerize your R Notebooks with Docker, for reproducible sharing, using renv for dependency management.View post to subscribe to the site’s newsletter.
-
Small Data: Creativity, Explainability & Precision

This post discusses the significance of small data in the context of data science and modeling, detailing tips and tricks for working with small data sets.View post to subscribe to the site’s newsletter.
-
Bayesian Time Series Interpolation

The third article in the series, I explore Bayesian modeling for multivariate time series interpolation with hierarchical models with Numpyro and Bambi.View post to subscribe to the site’s newsletter.
-
Genetic Algorithms with PyGAD and PyTorch
Deep dive into Genetic Algorithms (GAs), an optimization algorithm inspired by the concept of natural evolution, including using a GA to train a Pytorch model with the Pygad library.View post to subscribe to the site’s newsletter.
-
How to Choose a Distribution for your Regression Model

This article is all about distributions! In it, I explore the most common distributions including Gaussian, Uniform, Student-T, Gamma, and others. I also discuss their applications and when to choose them for regression modelling.View post to subscribe to the site’s newsletter.
-
Heteroscedastic Data – Part 2: Inference

In this article, I deal with complex heteroscedastic problems for data analysis and inference. With a simulated dataset to demonstrate, I tackle issues such as strong trends, non-linearity, non-normal target distributions, multiple seasonalities, and changing variance. I use the advanced techniques of Bayesian Spline Modelling and Bayesian Additive Regression Trees (BART), emphasizing their efficacy in…
-
Heteroscedastic Regression

In this article, I deal with complex heteroscedastic problems for data analysis and inference. With a simulated dataset to demonstrate, I tackle issues such as strong trends, non-linearity, non-normal target distributions, multiple seasonalities, and changing variance. I use the advanced techniques of Bayesian Spline Modelling and Bayesian Additive Regression Trees (BART), emphasizing their efficacy in…
-
Mutual Information: a powerful alternative to correlation

While Pearson Correlation is effective in identifying relationships during exploratory data analysis, Mutual Information (MI) offers a powerful alternative, capable of uncovering non-linear relationships between variables. Despite being harder to interpret, its implementation in Scikitlearn is worth exploring.
-
Mutual Information

While Pearson Correlation is effective in identifying relationships during exploratory data analysis, Mutual Information (MI) offers a powerful alternative, capable of uncovering non-linear relationships between variables. Despite being harder to interpret, its implementation in Scikitlearn is worth exploring.View post to subscribe to the site’s newsletter.
-
Working with Heteroscedastic Data

Heteroscedasticity, variance inconsistency across a related variable’s range, is often overlooked in data analysis. The two-part series explores handling heteroscedastic data through transformations, linear models, and model-based solutions, using LinkedIn engagements for instance. Techniques include Quantile Regression, Conditional Variance model, and common transformations like power or square root transformations.View post to subscribe to the site’s…